Choosing the right large language models today can feel overwhelming. With so many options promising better performance, accuracy, and speed, it’s hard to know which one actually delivers. If you’re trying to find the best model for your needs whether it’s writing, coding, or business automation, this guide breaks down the most popular large language models and helps you make a clear, confident decision.
For entrepreneurs looking beyond LLMs, this step-by-step guide on how to build an automated AI content business offers practical strategies and tools: Start your automated AI content business.
What Makes LLMs So Powerful?
LLM Models (Large Language Models) are advanced AI systems trained on massive datasets of text to understand, generate, and respond in natural language.
They can:
- Answer questions
- Write content
- Generate code
- Translate languages
- Assist with business tasks
In simple terms, large language models act like intelligent assistants that understand human language and produce meaningful responses based on context.
How Do large language models Work?
Large Language Models (LLMs) operate using advanced deep learning systems designed to recognize, interpret, and generate human language. At their core, these models rely on a neural network structure known as the transformer architecture, which enables them to process vast amounts of text efficiently and understand complex language patterns.
Below is a detailed explanation of how large language models function:
1. Large-Scale Training Process
LLMs are trained on extremely large collections of text data. This data may include books, research papers, publicly available websites, technical documentation, and other written materials.
During training, the model does not memorize text in the traditional sense. Instead, it learns statistical patterns such as how words relate to each other, how sentences are structured, and how ideas flow within paragraphs. The objective during training is typically to predict missing or next words in a sequence, which gradually teaches the system grammar, meaning, tone, and contextual relationships.
2. Contextual Understanding Through Transformers
Unlike older language systems that processed words one at a time, transformer-based models analyze entire sequences of text simultaneously.
This allows the model to:
- Recognize relationships between words that are far apart in a sentence
- Understand nuance, tone, and intent
- Capture meaning based on context rather than isolated keywords
For example, the word “bank” in a sentence about rivers is interpreted differently than “bank” in a sentence about finance. The transformer mechanism uses attention layers to determine which words influence each other most strongly.
3. Response Generation Mechanism
When a user provides a prompt, the LLM processes the input and converts it into numerical representations. The model then calculates probabilities for possible next words based on patterns learned during training.
Instead of choosing randomly, it selects words that statistically make sense within the given context. This process happens rapidly and repeatedly word by word until a complete response is formed.
The result is text that appears coherent, structured, and relevant to the user’s request.
4. Fine-Tuning and Alignment
After initial large-scale training, many LLMs undergo additional refinement. This stage often involves:
- Supervised fine-tuning with curated datasets
- Human feedback to improve clarity and usefulness
- Safety adjustments to reduce harmful or misleading outputs
This refinement stage improves reasoning ability, accuracy, and alignment with human expectations.
5. Continuous Model Improvements
Each new generation of large language models typically includes architectural optimizations, larger training datasets, improved reasoning algorithms, and expanded context windows.
These improvements allow newer versions to:
- Handle longer documents
- Provide more accurate answers
- Demonstrate stronger logical reasoning
- Perform complex tasks such as coding, analysis, and summarization more effectively
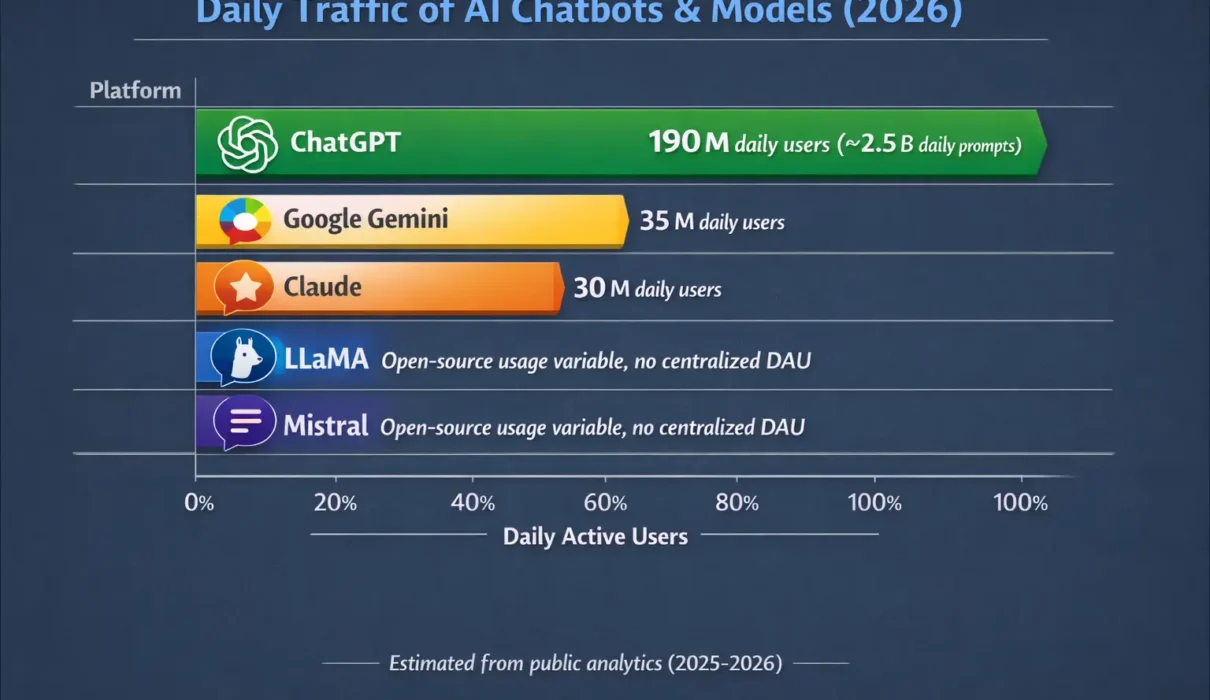
Image shows the daily base traffic to all popular large language models.
Popular LLM Models in 2026
Here are the most widely used popular LLM models today:
1. ChatGPT
Developed by OpenAI, ChatGPT is one of the most widely used and versatile large language models available today. It is designed to handle a wide range of tasks, from simple conversations to complex reasoning and problem-solving.
ChatGPT stands out because of its ability to understand context, follow instructions, and generate high-quality responses that feel natural and human-like. It is continuously improved with new versions, making it one of the most reliable AI tools for both individuals and businesses.
Key Strengths
- Strong reasoning and conversational ability
ChatGPT can understand complex queries and provide logical, structured answers, making it ideal for both beginners and professionals. - Excellent for writing and coding
It can generate blog posts, emails, scripts, and even debug or write code in multiple programming languages. - Wide range of integrations
ChatGPT is integrated into apps, tools, and platforms, allowing businesses to automate workflows and improve productivity.
Limitations
- Advanced features may require a paid plan
- Sometimes generates overly confident but incorrect answers
Best For
- Content creation (blogs, ads, emails)
- Coding and debugging
- Customer support automation
- General-purpose AI usage
2. Gemini
Built by Google, Gemini is a powerful LLM designed to work across multiple types of data, including text, images, and more. It is deeply integrated with Google’s ecosystem, making it especially useful for users already using Google products.
Gemini’s biggest advantage is its ability to process and combine different types of information, which makes it highly effective for research and real-time tasks.

Key Strengths
- Multimodal capabilities
Gemini can understand text, images, and other inputs, allowing it to perform more complex tasks than traditional models. - Deep Google integration
It works seamlessly with tools like Google Docs, Gmail, and Search, making workflows faster and more efficient. - Strong real-time data capabilities
Gemini can access and process up-to-date information, which is useful for research and decision-making.
Limitations
- Responses can sometimes be less consistent compared to competitors
- Performance may vary depending on the task
Best For
- Research and data analysis
- Productivity tasks within Google ecosystem
- Multimodal use cases (text + images)
- Real-time information queries
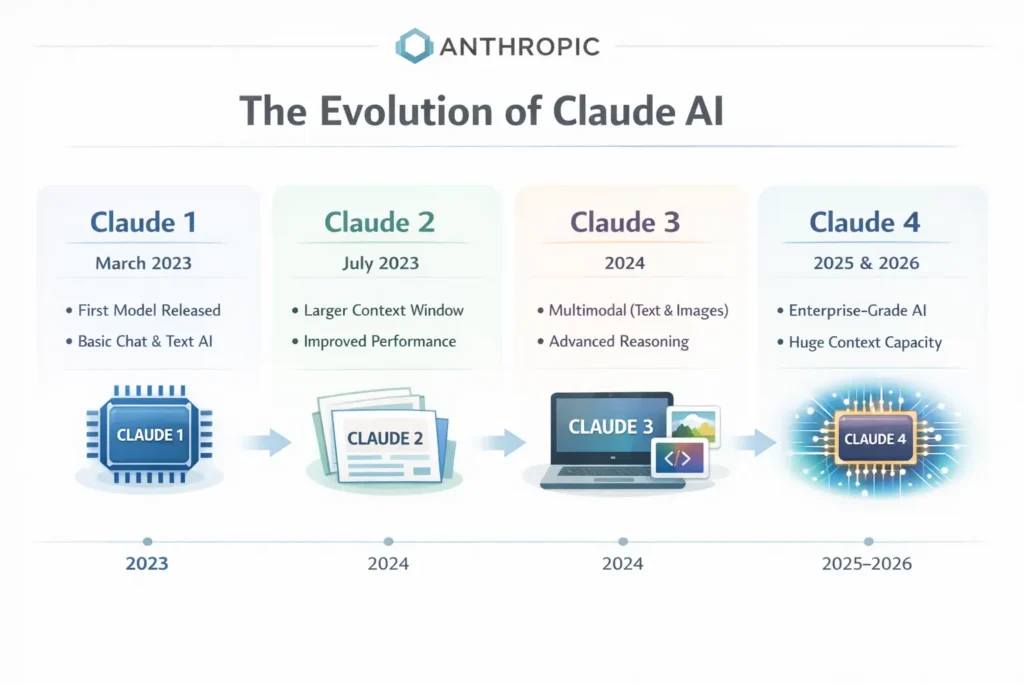
3. Claude
Created by Anthropic, Claude is designed with a strong focus on safety, reliability, and handling long pieces of content. It is particularly known for its ability to process large amounts of text while maintaining context.
Claude is often preferred by businesses that need accurate, thoughtful, and structured responses, especially when working with long documents or complex information.
Image shows the journey of Claude AI.
Key Strengths
- Large context window
Claude can analyze long documents, reports, and conversations without losing context, making it ideal for in-depth tasks. - High-quality long-form responses
It produces detailed, well-structured content that is useful for professional and business use. - Safety-focused design
Claude is built to minimize harmful or misleading outputs, making it more reliable in sensitive use cases.
Limitations
- Limited integrations compared to some competitors
- May be slower when processing very large inputs
Best For
- Document analysis and summarization
- Business reports and research
- Long-form content generation
- Safe and controlled AI applications
4. LLaMA
Developed by Meta, LLaMA is a family of open-source-friendly LLM models designed for flexibility and customization. Unlike proprietary models, LLaMA allows developers to modify and deploy the model according to their needs.
This makes LLaMA a popular choice for companies and developers who want more control over their AI systems.

Key Strengths
- Highly customizable
Developers can customize the model to perform specialized tasks across different industries. - Cost-effective
Since it is open-source-friendly, it reduces reliance on expensive API calls. - Strong developer ecosystem
A large community supports development, improvements, and integrations.
Limitations
- Requires technical knowledge to set up and manage
- Performance may depend on how it is fine-tuned
Best For
- Custom AI solutions
- Developers and AI engineers
- Businesses needing data privacy and control
- On-premise AI deployment
5. Mistral
From Mistral AI, Mistral is known for building efficient, high-performance LLM models that are lightweight and fast. It focuses on delivering strong performance while keeping computational costs low.
Mistral is gaining popularity among startups and developers who need scalable AI solutions without high infrastructure costs.
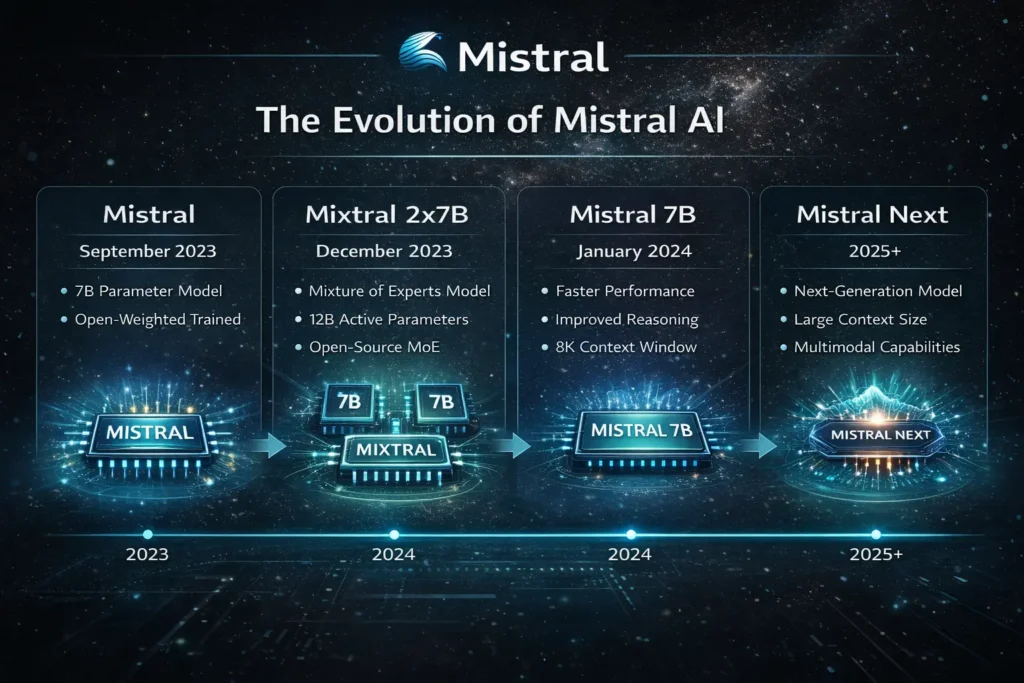
Key Strengths
- Lightweight and fast
Mistral models are optimized for speed, making them ideal for real-time applications. - Open-weight models
Developers can access and deploy models with more control compared to closed systems. - High performance per cost
Mistral delivers strong results while keeping operational costs low.
Limitations
- Smaller ecosystem compared to larger players
- Fewer integrations and tools available
Best For
- Startups and small businesses
- Efficient AI deployments
- Real-time applications
- Cost-sensitive projects
Final Insight
Each of these popular LLM models has its own strengths, and the right choice depends on your needs:
- ChatGPT → Best all-around performance
- Gemini → Best for research and multimodal tasks
- Claude → Best for long-form and safe outputs
- LLaMA → Best for customization and control
- Mistral → Best for efficiency and cost
If you’re choosing between them, focus on your use case, budget, and technical requirements rather than just popularity.
LLM Models Comparison Table
| Model | Best For | Strength | Weakness |
| ChatGPT | Writing & coding | Balanced performance | Paid tiers for best use |
| Gemini | Research & data | Real-time integration | Less consistent outputs |
| Claude | Long content | Large context window | Limited integrations |
| LLaMA | Development | Open-source flexibility | Requires setup |
| Mistral | Efficiency | Fast and lightweight | Smaller ecosystem |
How We Evaluated the Top LLMs
1. Performance
- ChatGPT offers balanced and reliable performance
- Gemini excels in real-time information
- Claude performs best with long inputs
2. Reasoning Ability
- ChatGPT provides strong logical reasoning
- Claude handles complex documents well
- Gemini continues improving in reasoning tasks
3. Speed
- Mistral and Gemini are generally faster
- ChatGPT balances speed and quality
- Claude may be slower with large contexts
4. Cost
- Open-source models like LLaMA and Mistral are cheaper
- Proprietary models may require subscriptions
5. Context Handling
- Claude leads with long-context understanding
- ChatGPT offers strong contextual awareness
- Gemini supports multimodal context
Which LLM Model Is Best for Different Use Cases?
Choosing the right model depends on your specific needs.
Best LLM Model for Writing
ChatGPT is ideal for blogs, marketing, and creative writing.
Best LLM Model for Coding
ChatGPT and Claude both perform well for coding tasks, with strong reasoning.
Best LLM Model for Business
Claude is excellent for analyzing reports and long documents.
Best LLM Model for Research
Gemini is useful due to its integration with real-time data.
Best Open-Source LLM Model
LLaMA and Mistral provide flexibility and cost efficiency.
Open Source vs Proprietary LLM Models
LLM models fall into two categories:
Open Source Models
Examples: LLaMA, Mistral
- More control
- Lower cost
- Requires technical expertise
Proprietary Models
Examples: ChatGPT, Gemini, Claude
- Easy to use
- High performance
- Subscription costs
Choosing between them depends on your budget, skills, and use case.
How to Choose the Right LLM Model
Follow these steps to select the best model:
- Define Your Goal
Writing, coding, research, or automation - Evaluate Performance
Check reasoning, accuracy, and output quality - Consider Cost
Balance features with your budget - Check Integration Needs
Ensure compatibility with your tools - Test Before Final Decision
Try multiple models to compare results
Future of LLM Models (2026 and Beyond)
The future of LLM Models is rapidly evolving.
Key trends include:
- More multimodal capabilities
- Better reasoning and accuracy
- Smaller, more efficient models
- Increased focus on AI safety
- Greater personalization
As technology advances, LLM models will become even more powerful and accessible for businesses and individuals.
FAQs
What are LLM models?
LLM models are AI systems trained on large datasets to understand and generate human-like language. They are used for writing, coding, answering questions, and automation.
Which LLM model is best?
The best model depends on your needs. ChatGPT is great for general use, Claude for long documents, and Gemini for research.
Is ChatGPT better than Gemini?
ChatGPT is better for writing and reasoning, while Gemini is stronger in real-time data and integration. The choice depends on your use case.
Are LLM models free?
Some LLM models offer free versions, but advanced features usually require paid plans. Open-source models can be used at lower cost but need technical setup.
What is the difference between LLM and AI?
AI is a broad field, while LLM models are a specific type of AI focused on understanding and generating text.
Conclusion:
There is no single best LLM model for everyone. The right choice depends on your goals, budget, and technical needs.
- Choose ChatGPT for versatility
- Choose Gemini for research and integration
- Choose Claude for long-form content
- Choose LLaMA or Mistral for customization
By understanding the strengths of each model, you can select the best option and unlock the full potential of modern AI.